- HOME
- Research
- Researcher's Profile
- Takafumi MIYASAKA
Researcher's Profile

- Project Associate Professor
- Takafumi MIYASAKA
- Global Climate Dynamics
Biography
| March 2006 | Ph.D., Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo (UTokyo) |
|---|---|
| April 2006 | Research Fellow, Center for Climate System Research, UTokyo |
| June 2006 | Business-Academia-Government Collaboration Researcher, Center for Climate System Research, UTokyo |
| April 2007 | Researcher, Graduate School of Science, UTokyo |
| December 2007 | Business-Academia-Government Collaboration Researcher, Graduate School of Science, UTokyo |
| April 2008 | Project Researcher, Graduate School of Science, UTokyo |
| April 2011 | Project Researcher, RCAST, UTokyo |
| April 2016 | Project Research Associate, RCAST, UTokyo (-2021.05) |
| April 2018 | Researcher, Japan Meteorological Business Support Center |
| April 2020 | Associate Senior Researcher, Japan Meteorological Business Support Center |
| June 2021 | Project Associate Professor, RCAST, UTokyo |
Research Interests
Climate characterized by weather and its seasonal transition shows regional characteristics. Since extreme weather occurs under regional climate, extreme weather also shows regional characteristics. Since Japan Islands extend meridionally and include mountain ranges and adjacent plains, climate and extreme weather show various regional characteristics in Japan. In global perspective, Japan is characterized by important climate system. Japan is surrounded by ocean and adjacent to warm and cool currents from south and north, respectively, and oceanic frontal zone. In addition, there is a strong upper-level westerly jet over Japan.
Local extreme weather tends to be influenced by large-scale atmospheric circulation, and large-scale atmospheric circulation can be related to counterpart in far region through remote influence. Therefore, understanding of global scale phenomena are often required for comprehensive understanding of regional scale phenomena. One example is influence of global warming on intensity of local heavy rainfall. Detail research for respective regions is required for more accurate understanding of local phenomena because of regional characteristics in climate.
Our research interests include 1) mechanisms of extreme weather and climate variability based on observations and 2) influence of global warming on them by using numerical simulations. Both climate change forced by global warming and climate variability arising internally in climate system are closely related to variability in ocean, since low-frequency variability tends to be associated with ocean, which has larger inertia than atmosphere. Therefore, we focus on atmosphere-ocean interaction and sea surface temperature variability. Another interest is high resolution reanalysis around Japan. I join a project to produce regional reanalysis data set, which clarify the past atmospheric condition estimated by observations and numerical simulation. This fundamental data set is important for more detail investigations of weather and climate in Japan.
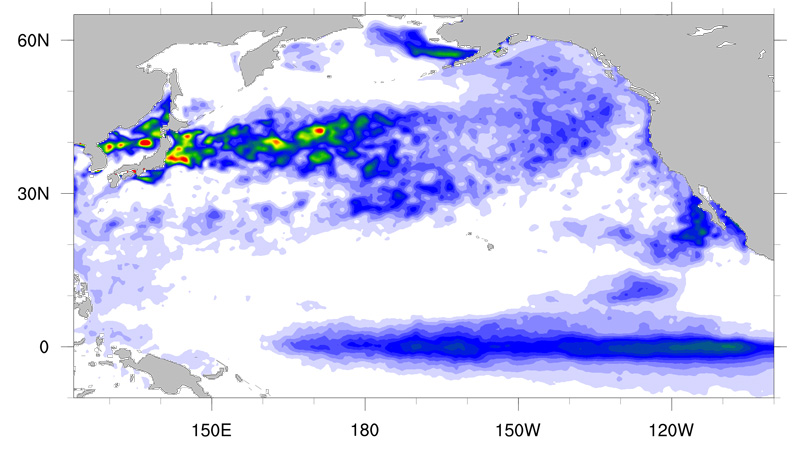
- Remarkable decadal variability of sea surface temprare especially in the mid-latitude
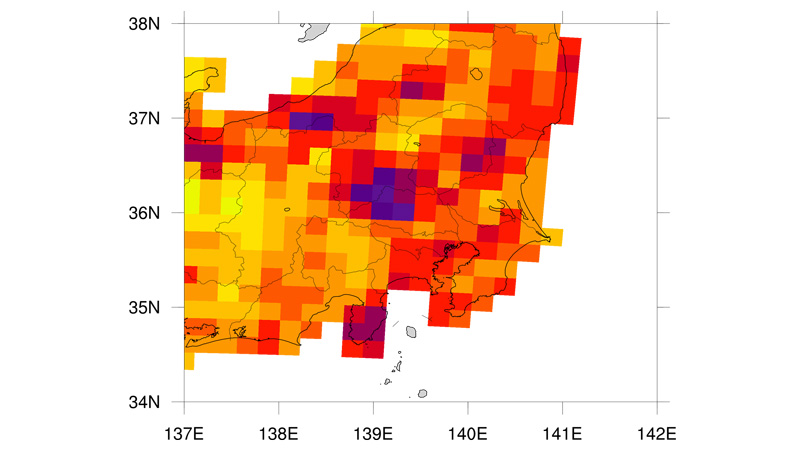
- Projection of extreme precipitation enhancement under 4-K warming climate
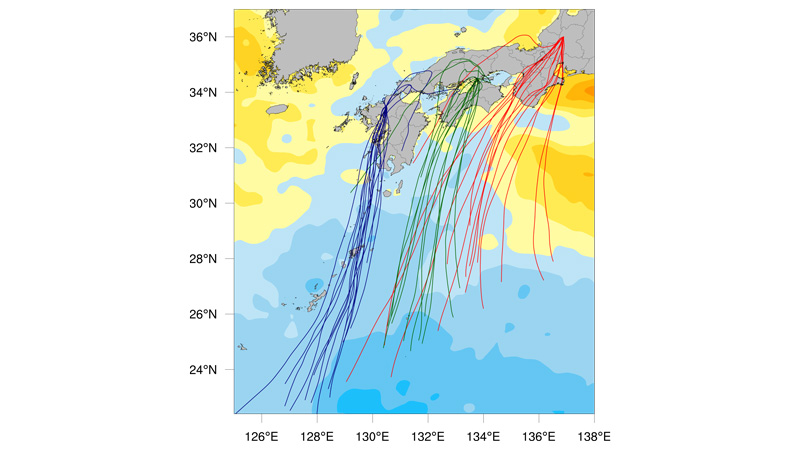
- 24-hour trajectories of air parcel into heavy precipitation areas and sea surface temperature anomaly in July 2018
Keywords
Climate variability, extreme weather, air-sea interaction

 atmos.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp
atmos.rcast.u-tokyo.ac.jp